News
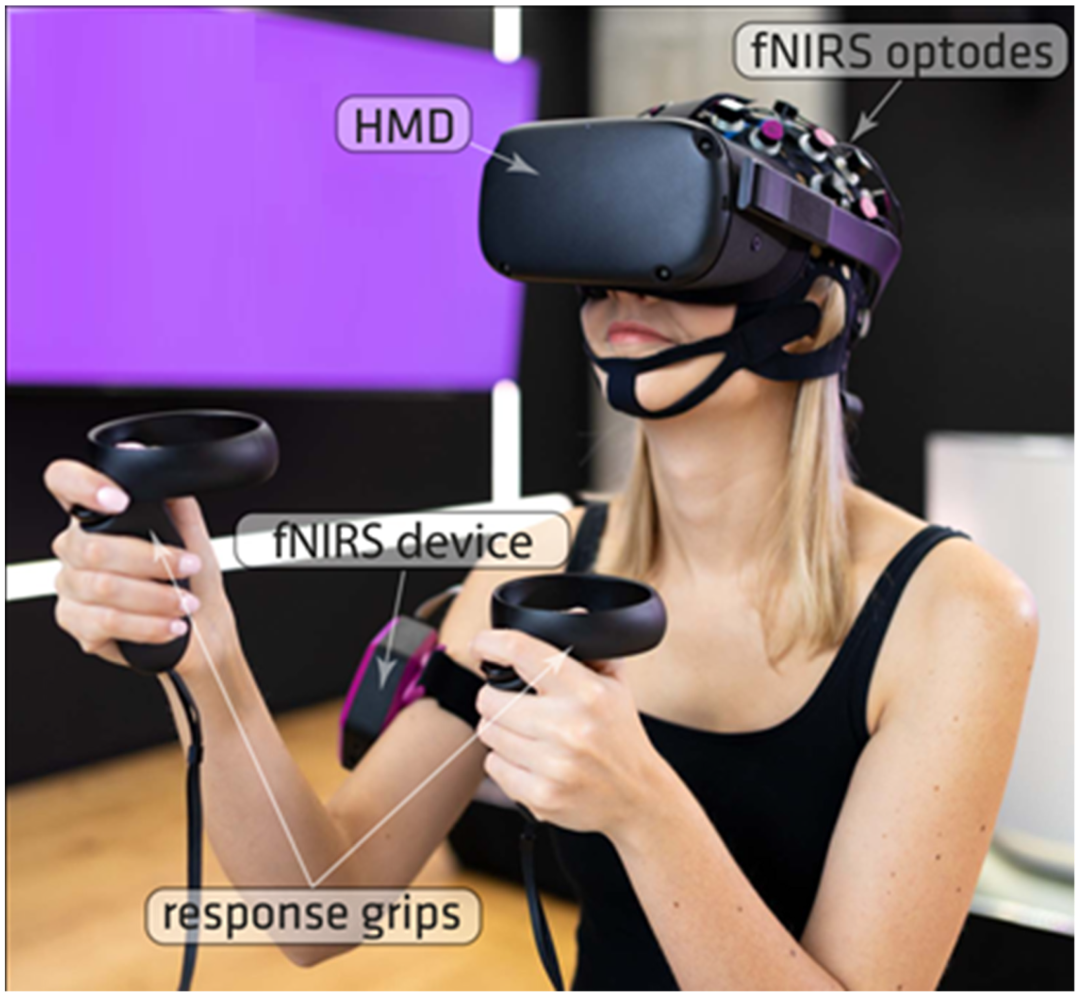

Attentional state recognition in virtual reality environments
Researchers from Poland have published an article in the journal Sensors that explores the practical combination of virtual reality (VR) and near-infrared technology. They designed an integrated experimental platform containing CW-fNIRS and head-mounted display (HMD) technologies and conducted experiments in virtual reality using a variant of the classic n-back task (2-back version). The results confirm that by combining fNIRS and HMD technologies, experimenters can effectively transfer experimental cognitive processes to a controlled VR environment. Research Background Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is one of the newest and fastest functional neuroimaging techniques that uses near-infrared light at wavelengths of 650-950 nm to measure hemodynamic responses in cortical brain regions. NIR systems typically use lasers or LEDs to emit continuous wave (CW) NIR light. VR technology has been used for the study and training of attentional skills, and there have been many case studies and papers combining VR and NIR technology. The feasibility of combining VR and FNIRS technologies to modulate attentional states through training procedures has been demonstrated. Identifying attentional states can be used to monitor the engagement of subjects in a task. The user's experience of interacting with the system can be measured by visual scales and questionnaires to measure their satisfaction. The hypothesis of this study. The difference in hemodynamic activity (HbO/HbR concentration changes) between enhanced attentional engagement (n-back task) and relaxation states in the DLFPC and MFG regions will be significantly higher than the opportunity threshold level for the study group. The user-system interaction experience (fNIRS+HMD) will be higher than the mean of the satisfaction assessment scale. Subjects Twelve subjects (10 females), aged 21-34 years (M = 24.82; SD = 4.38) participated in the experiment. All participants in the experiment were right-handed with normal bare and corrected visual acuity. Equipment NIR signals were recorded in a dual wavelength (760 and 850 nm) fnirs system ((Cortivision sp. z o.o., Lublin, Poland). A total of 16 LED sources and 10 detectors were used. Data processing for the online phase was performed on OpenViBE 3.1.0 (Inria Hybrid Team, Rennes, France) using a custom Python script. VR scenes were developed using the Unity3D engine and displayed on Oculus Quest (Facebook Technologies, Menlo Park, CA, USA). Statistical analysis of the results was performed using JASP software. The experimental setup consisted of wireless integrated VR goggles and a wearable fNIRS device. During data recording, participants were seated and the devices were wirelessly connected. Subjective satisfaction assessment The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) was used to assess the overall subjective satisfaction at the end of the experiment in both groups. The assessment was done on an 11-point scale". A modified version of the Quebec Assistive Technology User Evaluation (eQUEST 2.0) was used ...
Read more...
Read more...

Invitation Letter|Neural Engineering Management Colloquium Workshop (Round 1)
I. Neuroengineering Management Colloquium Workshop Over the past 70 years since the founding of our country, China's construction industry has created the world miracle of "home ownership" in the world's largest country in terms of population size, to which engineering management practitioners have made remarkable contributions. At present, the wheel of high-quality development of the construction industry has quietly arrived, which requires the practice of engineering management to gradually shift from "material-oriented" to "people-oriented". In this context, how to realize "people-oriented" has become a hot issue at the forefront of engineering management research. Neuromanagement in Engineering (Neuromanagement in Engineering) is based on the interdisciplinary theories of cognitive neurology, psychology, behavioral decision making, organizational behavior and engineering management, and integrates multidisciplinary research paradigms, combined with EEG, eye movement, NIR, VR, AR and other research tools, and adopts experiments, big data and subjective reports. It is a new research direction to achieve the goal of "human-oriented" engineering management by combining EEG, eye-movement, NIR, VR, AR and other research methods and adopting experimental, big data and subjective report data fusion collection and analysis methods to reveal the laws of human activities in engineering management activities. In order to promote the promotion and development of neuroengineering management-related research, build a platform for scholars in related fields to exchange and cooperate, promote the innovative integration of cognitive neuroscience, brain science and other related disciplines with engineering management, and promote the innovation of engineering management research methods, theories and paradigms, the first symposium on neuroengineering management is scheduled to be held in Chongqing from June 3 to 4, 2023. The conference is organized by the Neural Engineering Management Research Committee, hosted by the School of Management Science and Real Estate of Chongqing University and the International Research Center for Sustainable Construction of Chongqing University, and organized by the School of Civil Engineering and Water Resources of Tsinghua University, the Department of Construction and Real Estate of Hong Kong Polytechnic University, the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering of City University of Hong Kong, the School of Civil Engineering of Tongji University, the School of Management of Shanghai University, the School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics of Jiangsu University, the School of Management of Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, and the School of Civil Engineering of Chongqing University. Ltd. Experts from related fields are warmly welcomed to attend the conference! 1、Workshop theme Neuromanagement in Engineering: It is one of the latest research directions of neuromanagement, based on the theories of cognitive neuroscience, psychology, behavioral decision making, organizational behavior and engineering management, combined with EEG, eye movement, near infrared (fNIRS), VR, AR and other devices, using experiments, big data (including video analysis and subjective reports) and other methods. The workshop is based on the theories of neuroengineering management and engineering management, including EEG, eye movement, near-infrared (fNIRS), VR, AR, etc., and adopts experimental, big data (including video analysis) and subjective report methods to study human activities in engineering management activities, including behavior, psychology, physiology (including health), human-computer interaction, etc., in order to achieve the ultimate goal of "human-oriented" in engineering management. Based on the basic concept of neuroengineering management, this workshop will bring you the case study of psychological technology in neuroengineering management and the principles and characteristics of eye-tracking, EEG and NIR technology. We are looking forward to exchanging and discussing with all the guests on this topic. 2、Organization Hosted by Neuroengineering Management Research Committee Undertaker. Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. Wuhan Institute of Human Factors Engineering and Technology
3、Time and place Time: June 3, 2023 Venue: Chongqing University (174 Shazheng Street, Shapingba District, Chongqing, China) Note: This workshop will be held in conjunction with the First Symposium on Neuroengineering Management, and there is no fee for the workshop.
4、Workshop content Time Lecturer Content Summary June 3, 15:00-16:00 Shan Keqiu Application of psychological techniques in neuroengineering management and case studies Practical application of NIR, EEG and eye movement techniques in neuroengineering management June 3, 16:10-17:10 Can Jin Principles and characteristics of eye movement, EEG and NIR techniques A detailed introduction to the principles and characteristics of EEG, NIR and eye movement techniques. Detailed introduction June 3, 17:10-17:30 Shan Keqiu, Jin Can Discussion and demonstration of the instruments and trial operation of the relevant instruments 5、Lecturer introduction Shan Keqiu: Theoretical consultant of Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd, Master of Psychology of Dublin University Jin Can: Theoretical consultant of Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. 6、Workshop Contact Xia Haiyan:18911883058 Li Jiahua:18500350004 II. Graduate Student Innovation Fund Ltd. will fund the "Hengzhi-Neural Engineering Management Seminar Postgraduate Research Innovation Fund" (5000/item for PhD students and 3000/item for master students), and will provide differential funding to the students who participate in the postgraduate forum. 1. Name of the fund. Everloyal-NME-202301) 2、Number of people funded. Doctoral Research Innovation Fund: 3 persons, RMB 5,000 each Master's Research Innovation Fund: 5 persons, RMB 3,000 each 3、Fund content. (1) This fund is jointly established by Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd. and the Academic Committee of Neuroengineering Management Symposium to support young researchers in the field of neuroengineering management-related research. (2) Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd. provides necessary scientific training and services to the postgraduate research innovation fund supporters, and gives priority to providing support in equipment rental, experimental assistance, data analysis, etc. (3) The fund project funds will be directly allocated by Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd. to the researcher's unit and managed as a joint scientific research project, and the research results published under the project funding should be marked as fund project - horizontal. (4) Beijing Hengzhi Science and Technology Co., Ltd. will assist in the industrial transformation of the innovative achievements in the field of neural engineering management and promote the cooperation between industry, academia and research. (5) The project funding period will last for one year from the establishment of the project, and a special sub-forum will be set up in the "Second Symposium on Neuroengineering Management" for the postgraduate research innovation fund, and the project funders will be invited to make a summary report. III.Neural Engineering Management Symposium Conference Information The conference will be held offline and the basic information of the conference is as follows Hosted by Neuroengineering Management Research Committee
Undertaker. School of Management Science and Real Estate, Chongqing University International Research Center for Sustainable Construction, Chongqing University Co-organizers. School of Civil Engineering and Water Resources, Tsinghua University Department of Construction and Real Estate, Hong Kong Polytechnic University Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, City University of Hong Kong School of Civil Engineering, Tongji University School of Management, Shanghai University School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Jiangsu University School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology School of Management, Chongqing University Research Base of Language Cognition and Language Application, Wuhan Institute of Human Factors Engineering and Technology, Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. Note: This seminar is exclusively supported by Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. 1、Time and place (1) Conference Venue: Chongqing University, School of Management Science and Real Estate Building (2) Conference Program: June 3, 2023 - June 4, 2023 (3) Deadline for submission of long abstracts: April 15, 2023 2、Conference theme (1) Research on neural engineering management (2) Research on "human-centered" engineering management 3、Conference organization ...
Read more...
3、Time and place Time: June 3, 2023 Venue: Chongqing University (174 Shazheng Street, Shapingba District, Chongqing, China) Note: This workshop will be held in conjunction with the First Symposium on Neuroengineering Management, and there is no fee for the workshop.
4、Workshop content Time Lecturer Content Summary June 3, 15:00-16:00 Shan Keqiu Application of psychological techniques in neuroengineering management and case studies Practical application of NIR, EEG and eye movement techniques in neuroengineering management June 3, 16:10-17:10 Can Jin Principles and characteristics of eye movement, EEG and NIR techniques A detailed introduction to the principles and characteristics of EEG, NIR and eye movement techniques. Detailed introduction June 3, 17:10-17:30 Shan Keqiu, Jin Can Discussion and demonstration of the instruments and trial operation of the relevant instruments 5、Lecturer introduction Shan Keqiu: Theoretical consultant of Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd, Master of Psychology of Dublin University Jin Can: Theoretical consultant of Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. 6、Workshop Contact Xia Haiyan:18911883058 Li Jiahua:18500350004 II. Graduate Student Innovation Fund Ltd. will fund the "Hengzhi-Neural Engineering Management Seminar Postgraduate Research Innovation Fund" (5000/item for PhD students and 3000/item for master students), and will provide differential funding to the students who participate in the postgraduate forum. 1. Name of the fund. Everloyal-NME-202301) 2、Number of people funded. Doctoral Research Innovation Fund: 3 persons, RMB 5,000 each Master's Research Innovation Fund: 5 persons, RMB 3,000 each 3、Fund content. (1) This fund is jointly established by Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd. and the Academic Committee of Neuroengineering Management Symposium to support young researchers in the field of neuroengineering management-related research. (2) Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd. provides necessary scientific training and services to the postgraduate research innovation fund supporters, and gives priority to providing support in equipment rental, experimental assistance, data analysis, etc. (3) The fund project funds will be directly allocated by Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd. to the researcher's unit and managed as a joint scientific research project, and the research results published under the project funding should be marked as fund project - horizontal. (4) Beijing Hengzhi Science and Technology Co., Ltd. will assist in the industrial transformation of the innovative achievements in the field of neural engineering management and promote the cooperation between industry, academia and research. (5) The project funding period will last for one year from the establishment of the project, and a special sub-forum will be set up in the "Second Symposium on Neuroengineering Management" for the postgraduate research innovation fund, and the project funders will be invited to make a summary report. III.Neural Engineering Management Symposium Conference Information The conference will be held offline and the basic information of the conference is as follows Hosted by Neuroengineering Management Research Committee
Undertaker. School of Management Science and Real Estate, Chongqing University International Research Center for Sustainable Construction, Chongqing University Co-organizers. School of Civil Engineering and Water Resources, Tsinghua University Department of Construction and Real Estate, Hong Kong Polytechnic University Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, City University of Hong Kong School of Civil Engineering, Tongji University School of Management, Shanghai University School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Jiangsu University School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology School of Management, Chongqing University Research Base of Language Cognition and Language Application, Wuhan Institute of Human Factors Engineering and Technology, Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. Note: This seminar is exclusively supported by Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co. 1、Time and place (1) Conference Venue: Chongqing University, School of Management Science and Real Estate Building (2) Conference Program: June 3, 2023 - June 4, 2023 (3) Deadline for submission of long abstracts: April 15, 2023 2、Conference theme (1) Research on neural engineering management (2) Research on "human-centered" engineering management 3、Conference organization ...
Read more...

Northwest A&F University of Science and Technology | Behavioral Economics and Policy Simulation Lab is officially put into use, and Hengzhi Technology is helping to build it
The Behavioral Economics and Policy Simulation Laboratory of Northwest A&F University of Science and Technology (NWFUST) is built by the School of Economics and Management of NWFUST with the goal of serving scientific research and teaching, aiming at exploring the mystery of economic behavior and decision-making through scientific experimental means, providing a platform for researchers to conduct scientific research and study, and promoting the development of basic economic theories and innovation of research methods. The laboratory is located in Room C620 of the Liberal Arts Building of Northwest A&M University, with four functional areas: Neuroeconomics Laboratory, Behavioral Economics Laboratory, Virtual Reality (VR) Laboratory and Policy Simulation Laboratory, which have been officially put into use.
In the morning of February 26, dozens of experts from many universities in China, such as Zhejiang University, Renmin University of China, China Agricultural University and Huazhong Agricultural University, visited the site in person. While experiencing virtual scenes and marveling at the charm of science and technology, they put forward many constructive and valuable suggestions on how the laboratory can be combined with the agricultural and forestry economic management disciplines and applied to scientific research.
In this regard, Professor Ren Yanjun reported in detail the basic situation of the laboratory construction, operation and management ideas and future development direction. The delegation experienced the virtual (VR) reality Cave system, the Cortivision blood oxygen fusion imaging system in Poland, the Tobii ophthalmoscope in Sweden and other experimental equipment, and expressed full affirmation of the laboratory construction work. At the same time, they made corresponding suggestions on laboratory management, future development, talent training, equipment maintenance, etc. They also hoped that the laboratory would adhere to the basic concept of interdisciplinary and cross-border integration, base on the frontier of disciplines, enhance the domestic competitiveness and international influence of the first-level disciplines mainly in agriculture and forestry economic management, cultivate high-quality talents and produce high-quality research results.
Link to original article. Focus on Economics and Management | Behavioral Economics and Policy Simulation Lab Opens
Company Profile Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd, invested by China Science (Guangdong) Science Group, relying on the technical background of Guangdong Institute of Human Factors Technology and Wuhan Institute of Human Factors Engineering Technology, is a new type of high-tech enterprise based on psychological human factors, driving human factors, biomechanics, user experience, virtual reality and other directions, integrating production, research and development, sales and technical services, has been successfully selected in Zhongguancun High-tech enterprise list.
The driving human factors system, virtual reality graphic editing software, light environment psychological assessment system and psychological and human factors experimental teaching system developed by Hengzhi Technology have entered the domestic market. As the sole agent of Poland Cortivision NIR, Russia Mitsar EEG in China, the sole agent of Italy BTS surface electromyography and other biomechanical and gait analysis products in China, and the sole agent of Netherlands Noldus Behavioral Science, Sweden Tobii Eye Motion Instrument, Netherlands MindMedia Physiology and Biofeedback, US Biopac Physiology, US ETT The domestic licensed agent of products such as olfactory/taste stimulator. The high-tech products operated have served the top universities and the highest level of scientific research units in China, including Tsinghua University, Beijing Normal University, Northeast Normal University, Yanshan University, Qiyuan Laboratory, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen University of Technology, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Shanghai University, the Second Institute of Aerospace, 27 and 28 of China Electronics Technology Group, while providing technical support for ink Netease, Huawei technology to provide technical support, in the field of talent training, scientific research cooperation, transformation of results and other scientific and technological areas of continuous in-depth cooperation.
Follow us: This article comes from the WeChat public number: EVERLOYAL ...
Read more...
In the morning of February 26, dozens of experts from many universities in China, such as Zhejiang University, Renmin University of China, China Agricultural University and Huazhong Agricultural University, visited the site in person. While experiencing virtual scenes and marveling at the charm of science and technology, they put forward many constructive and valuable suggestions on how the laboratory can be combined with the agricultural and forestry economic management disciplines and applied to scientific research.
In this regard, Professor Ren Yanjun reported in detail the basic situation of the laboratory construction, operation and management ideas and future development direction. The delegation experienced the virtual (VR) reality Cave system, the Cortivision blood oxygen fusion imaging system in Poland, the Tobii ophthalmoscope in Sweden and other experimental equipment, and expressed full affirmation of the laboratory construction work. At the same time, they made corresponding suggestions on laboratory management, future development, talent training, equipment maintenance, etc. They also hoped that the laboratory would adhere to the basic concept of interdisciplinary and cross-border integration, base on the frontier of disciplines, enhance the domestic competitiveness and international influence of the first-level disciplines mainly in agriculture and forestry economic management, cultivate high-quality talents and produce high-quality research results.
Link to original article. Focus on Economics and Management | Behavioral Economics and Policy Simulation Lab Opens
Company Profile Beijing Hengzhi Technology Co., Ltd, invested by China Science (Guangdong) Science Group, relying on the technical background of Guangdong Institute of Human Factors Technology and Wuhan Institute of Human Factors Engineering Technology, is a new type of high-tech enterprise based on psychological human factors, driving human factors, biomechanics, user experience, virtual reality and other directions, integrating production, research and development, sales and technical services, has been successfully selected in Zhongguancun High-tech enterprise list.
The driving human factors system, virtual reality graphic editing software, light environment psychological assessment system and psychological and human factors experimental teaching system developed by Hengzhi Technology have entered the domestic market. As the sole agent of Poland Cortivision NIR, Russia Mitsar EEG in China, the sole agent of Italy BTS surface electromyography and other biomechanical and gait analysis products in China, and the sole agent of Netherlands Noldus Behavioral Science, Sweden Tobii Eye Motion Instrument, Netherlands MindMedia Physiology and Biofeedback, US Biopac Physiology, US ETT The domestic licensed agent of products such as olfactory/taste stimulator. The high-tech products operated have served the top universities and the highest level of scientific research units in China, including Tsinghua University, Beijing Normal University, Northeast Normal University, Yanshan University, Qiyuan Laboratory, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen University of Technology, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Shanghai University, the Second Institute of Aerospace, 27 and 28 of China Electronics Technology Group, while providing technical support for ink Netease, Huawei technology to provide technical support, in the field of talent training, scientific research cooperation, transformation of results and other scientific and technological areas of continuous in-depth cooperation.
Follow us: This article comes from the WeChat public number: EVERLOYAL ...
Read more...

Robots walk like people! Cross research at East China Normal University hits the algorithm key
Professor Shuguang Kuai's team at East China Normal University has used virtual reality combined with computational modeling to skillfully quantify human social walking behavior and further designed an algorithm based on human behavioral characteristics, significantly improving the anthropomorphic nature of robots and human-robot interaction experience, effectively solving the problem of integrating robots into social scenarios, building a link between human behavior theory and navigation algorithms, and realizing the This work is a leap from concepts and models to algorithms in human social mobility theory. This cross-cutting scientific research spanning humanities, science and engineering was published in the leading international computer science journal Nature - Machine Intelligence (Nature Machine Intelligence) was published on. How can robots enable high-quality social interaction? With the advent of the smart era, service robots are increasingly coming into human life and are expected to become the right-hand man of human life. How to make robots more human, better understand people and have high-quality social interactions with them has become a key and difficult problem in the field of service robots. To solve this challenge, it is necessary to translate the theoretical concepts of human social interaction behavior into algorithms that can be implanted into robotic platforms. To address this challenge, theProfessor Shuguang Kuai's research team from the School of Psychological and Cognitive Sciences and the Institute of Brain Science and Educational Innovation at East China Normal University has successfully constructed a virtual realityAn ideal experimental scenario for measuring social behaviorThe effective quantification and modeling of human social walking behavior, and its algorithmic implantation into the navigation platform of robots, has achieved a three-stage leap from conceptualization, computation to engineering of human science theories. Human social competence has an irreplaceable advantage over current artificial intelligence algorithms. This advantage is best demonstrated in the natural behavior of walking. "Hypothetically, in a social scenario, humans would walk based on modesty and try to avoid interfering with the social interactions of others, even though doing so might cause us to take long detours and consume more time and energy." Such behaviors and decisions, which are rare for humans, are quite challenging for robots, and how to make robots have human-like social capabilities so as to enhance the anthropomorphic nature of robots and the experience of human-robot interaction is an important challenge that needs to be addressed in the current field. From human social behavior to robotic navigation algorithms In response to this challenge, this research work aims to address two important scientific and technical questions within this framework.The first is how to quantify and model human social walking behavior and build quantitative models to predict human walking paths, and the second is how to implant these models into engineering algorithms to achieve enhancements to robot navigation algorithms. To address the first problem, although the fields of psychology, anthropology, and sociology have paid attention to human social interaction behavior for a long time and established many theories. However, these theories mostly stay at the level of phenomenal descriptions and lack complete quantitative computational models. The research team cleverly used cutting-edge virtual reality technology combined with traditional experimental psychology research methods to construct an ideal social walking experimental scenario in a virtual scene, and used this experimental scene to quantitatively measure the human social interaction space and social walking characteristics. On the basis of the behavioral experimental results, the team members further used computational modeling to construct a mathematical model of human walking behavior, and proposed a Social Locomotion Model based on individual social space, and demonstrated the robustness of the model in complex social scenarios in several virtual environments and real dynamic scenarios. In the second problem, after obtaining the computational model of social walking behavior, the research team algorithmized the model based on the actual engineering requirements and implanted it into the robot platform for verification and optimization to test whether the algorithm based on human intelligence can improve the human evaluation of robot sociality and humanoidity. The results of the study demonstrate in many ways that the computational model based on human behavioral characteristics can effectively improve the experience of human-robot interaction, as well as the humanoid and social aspects of the robot. A Behavioral Evaluation Platform for Robots New breakthroughs in cross-disciplinary fields With the development of socio-economic level and the improvement of people's living standard, the development of science and technology has moved from simply enhancing production capacity to leading the high-quality and harmonious development of human society. In such a new historical period, the importance and necessity of cross-fertilization of arts and science disciplines has become more and more prominent. Some members of the research team (from left: Mingyuan Yan, Mingcheng Miao, Shuguang Kuai, Chen Zhou and Qi Jan) Recently, the research results of this cross-science research spanning humanities, science and engineering were published in the leading international computer science journal Nature - Machine Intelligence (Nature Machine Intelligence) was published. Prof. Shuguang Kuai is the corresponding author of the paper, postdoctoral student Chen Zhou is the first author of the paper, and PhD student Mingcheng Miao, undergraduates Xinran Chen and Yifei Hu, and current undergraduates Qi Yan and Mingyuan Yan are co-authors of the paper. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Excellent Youth Program (32022031), the Major Project of Basic Research of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (19JC1410101), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under the Surface Project (2021M701227). The results of Prof. Shuguang Kuai's team at East China Normal University are published inNature Machine Intelligence Based on psychological theory and technology, Professor Shuguang Kuai has built a multidisciplinary cross-fertilization research team by integrating virtual reality and computer science, dedicated to quantifying a series of abstracted and conceptualized humanities theories by means of the latest intelligent technologies, and using humanities ideas to stimulate and guide breakthroughs in science and technology. The research team has designed a series of new research paradigms to computationalize and engineer humanities theories in recent years, and the related results have been published in Psychology (Nature Human Behaviour), neuroscience (Journal of Neuroscience), and Computer Science (Nature Machine IntelligenceThe research team has become a distinctive research team in the field of interdisciplinary research in the arts and sciences by appearing in high level international journals in the field of science and technology. Attachment.Human-behaviour-based social locomotion model improves the humanization of social robots Source丨East China Normal University ...
Read more...
Read more...

Professor Zhang Tong of Shenyang Agricultural University led a team to visit Hengzhi Technology to explore the road of multi-disciplinary integration and innovation
The grass grows and the warbler flies in February, and the willows are drunk with spring smoke. The green silk ribbons hanging down from the trees are made of jasper. I don't know who cut out the fine leaves, but the spring breeze in February is like scissors. On February 24, Beijing Hengzhi Technology welcomed the first batch of valuable guests in early spring: Professor Zhang Tong and his disciples from the College of Forestry of Shenyang Agricultural University. During this visit, Prof. Zhang Tong and his group deeply understood the background of science and technology industry as well as innovative technology and products of Hengzhi Technology, and exchanged the R&D path and achievements of the company in multi-discipline integration and innovation. In the company's exhibition hall, they visited a series of achievements based on psycho-human factors and user experience, including Cortivision NIR, BTS surface EMG and other devices. Prof. Zhang Tong said that the research and production work conducted by Hengzhi Technology has largely broken through the limitations of a single technical field and advocated multi-disciplinary cross-fertilization innovation, and this innovation model has positive significance for promoting both technological innovation and industrial upgrading. This visit also gave them a deeper understanding and consideration of the idea of multi-disciplinary technology integration and innovation. The innovation model of Hengzhi Technology was highly recognized and appreciated by Prof. Zhang Tong's team, and it also provided more ideas and possibilities for the future cooperation and communication between Shenyang Agricultural University College of Forestry and Hengzhi Technology. We believe that with the joint efforts of both sides, we will achieve more remarkable results in promoting scientific and technological innovation and industrial upgrading. We thank Prof. Zhang Tong's team for their trust and support to our company, which is not only the motivation and source for us to keep moving forward, but also a constant and sincere responsibility and commitment. As always, Hengzhi Technology will do its best to provide more comprehensive, better quality and more efficient customer service and support, to continuously surpass ourselves and create greater value for the society. Company Profile Beijing Hengzhi Technology, invested by China Science (Guangdong) Science Group, relying on the technical background of Guangdong Institute of Human Factors Technology and Wuhan Institute of Human Factors Engineering Technology, is a new type of high-tech enterprise based on psychological human factors, driving human factors, biomechanics, user experience, virtual reality and other directions, integrating production, research and development, sales and technical services, has been successfully selected in the Zhongguancun high-tech enterprise list.
The driving human factors system, virtual reality graphic editing software, light environment psychological assessment system and psychological and human factors experimental teaching system developed by Hengzhi Technology have entered the domestic market. As the sole agent of Poland Cortivision NIR, Russia Mitsar EEG in China, the sole agent of Italy BTS surface electromyography and other biomechanical and gait analysis products in China, and the sole agent of Netherlands Noldus Behavioral Science, Sweden Tobii Eye Motion Instrument, Netherlands MindMedia Physiology and Biofeedback, US Biopac Physiology, US ETT The domestic licensed agent of products such as olfactory/taste stimulator. The high-tech products operated have served the top universities and the highest level of scientific research units in China, including Tsinghua University, Beijing Normal University, Northeast Normal University, Yanshan University, Qiyuan Laboratory, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen University of Technology, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Shanghai University, the Second Institute of Aerospace, 27 and 28 of China Electronics Technology Group, while providing technical support for ink Netease, Huawei technology to provide technical support, in the field of talent training, scientific research cooperation, transformation of results and other scientific and technological areas of continuous in-depth cooperation. This article is from WeChat public number: Everloyal ...
Read more...
The driving human factors system, virtual reality graphic editing software, light environment psychological assessment system and psychological and human factors experimental teaching system developed by Hengzhi Technology have entered the domestic market. As the sole agent of Poland Cortivision NIR, Russia Mitsar EEG in China, the sole agent of Italy BTS surface electromyography and other biomechanical and gait analysis products in China, and the sole agent of Netherlands Noldus Behavioral Science, Sweden Tobii Eye Motion Instrument, Netherlands MindMedia Physiology and Biofeedback, US Biopac Physiology, US ETT The domestic licensed agent of products such as olfactory/taste stimulator. The high-tech products operated have served the top universities and the highest level of scientific research units in China, including Tsinghua University, Beijing Normal University, Northeast Normal University, Yanshan University, Qiyuan Laboratory, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen University of Technology, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Shanghai University, the Second Institute of Aerospace, 27 and 28 of China Electronics Technology Group, while providing technical support for ink Netease, Huawei technology to provide technical support, in the field of talent training, scientific research cooperation, transformation of results and other scientific and technological areas of continuous in-depth cooperation. This article is from WeChat public number: Everloyal ...
Read more...

Cognition | Social Statistical Learning Effects in Joint Action
From celestial movements to human life, the environment we live in contains complex and changing inner rules. Learning and mastering these rules is an important way for individuals to adapt to their environment and survive well, i.e., statistical learning. To date, however, most statistical learning research has been based on the individual level, with little exploration of the mechanisms of statistical learning in social settings, especially in joint action scenarios with others.In everyday life, people often need to identify and learn rules not only for their own task information, but also for acquiring task information from others.For example, four-handed joint playing in music performance. In order to explore the above joint statistical learning phenomenon, Professor Wang Jun's team at the School of Psychology, Zhejiang Normal University has conducted an in-depth study in the above direction, and the related results were published in the international well-known journal of psychology, Cognition. The study combines social learning transfer and the serial response-time paradigm in statistical learning.Experiment 1 used a joint practice scenario in which a stimulus stream containing two fixation sequences was assigned to two participants, in which each participant was required to practice only one of the fixation sequences in the stimulus stream without pressing a key in response to the fixation sequence of the peer task. After joint practice, individuals were able to acquire not only the rules of their own practice sequences (referred to as direct learning), but also the rules of their peers' practice sequences (referred to as indirect learning), as evidenced by a significant decrease in response time to both self- and others' task sequences. To further explore and validate the cognitive mechanisms of socio-statistical learning, i.e., shared representations, the present study systematically manipulated the scenarios of the practice process by separately employingSingle scenario(single subjects completed the learning phase alone, Experiment 2), theThe presence of others(completing the learning phase with a passively observing peer, Experiment 3), theBelief Scenarios(Imagine completing the learning phase with a partner, Experiment 4), theInconsistent Intent Scenario(Peers completed the color identification task without rules, Experiment 5) andBaseline scenario(single subjects completed all stages alone, Experiment VI). It was found that subjects in the belief scenario (Experiment IV) showed the same socio-statistical learning effect thatThat is, direct learning and indirect learning effects were produced. In contrast, in the other scenarios (Experiment 2, Experiment 3, Experiment 5, and Experiment 6), subjects were able to acquire only their own task rules and were unable to acquire peer or task-irrelevant rules. This study enriches existing statistical learning scenarios from a social interaction perspective and expands the representational content of existing common theories.Zheng Zheng, a doctoral student in Prof. Wang Jun's group, is the first author of the paper, and Prof. Wang Jun is the corresponding author of the paper. This study is supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Philosophy and Social Science Cultivation Laboratory "Zhejiang Provincial Child and Youth Mental Health and Crisis Intervention Intelligent Laboratory", and funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Philosophy and Social Science Leading Talents Cultivation Special Project (21YJRC09ZD). " Thesis information. Zheng, Z., & Wang, J.* (2023). Co-actors represent each other's task regularity through social statistical learning. Cognition, 235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cognition.2023.105411 This article is from the WeChat public number: EVERLOYAL ...
Read more...
Read more...

Brain-X: The submission system ScholarOne is officially online! Welcome to submit articles!
1 Introduction to the journal Brain-X (Provisional ISSN: 2835-3153, Cross-Cutting Brain Science) is a new multi-scientific English-language academic journal founded in 2022 by young scientists in the field of brain science/neuroscience/neurology at home and abroad, and published by Wiley Publishing Group. The editor-in-chief and associate editors are the editors-in-chief of several SCI journals, and the editorial board is composed ofBrain Science / Neuroscience/NeurologyThe Brain-X is dedicated to reporting on the latest developments in the field of Brain-X is dedicated to reporting onInterdisciplinaryfor the research contentBrain Science / Neuroscience / Neurologyinnovations in the field of brain science/neuroscience/neurology, aiming atCross-fertilization research with different disciplines such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, information, engineering and materials, and psychology(1+X mode)We will build a platform for academic exchange. Brain-XInitial periodGoal: To develop into a high impact (IF between 10 and 15) journal in the cross-cutting sciences. 2 Submission System After more than 1 month of testing, theBrain-XThe submission system ScholarOne Manuscripts (S1M for short) is now live! The submission site (available by clicking on "Read the original article"): https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/brain-x Figure 1 Pre-login interface Figure 2 Editorial post-login interface This article is from WeChat public number:恒挚科技EVERLOYAL ...
Read more...
Read more...
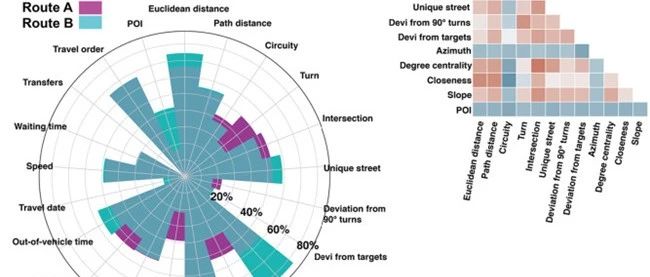
Academic Achievements | Spatio-temporal brain perception for public transportation travel
1 Content guide Public transportation travel benefits urban systems in many ways, such as reducing traffic congestion, reducing air pollution, and saving energy. The built environment of a city and the cost of travel time are considered to be the two key categories of factors that influence people's travel preferences and behavior during transportation trips. Therefore, understanding people's feelings and perceptions about the spatial and temporal characteristics of public transportation travel can not only improve the supply and operation of public transportation, but also encourage more people to use green and sustainable travel modes and increase travel well-being. In recent years, neuroimaging methods, led by functional magnetic resonance (fMRI), have been increasingly applied to urban science (e.g., urban well-being, landscape assessment, and navigation, among a range of other topics) to capture the connections between the human brain and urban perception and behavior. In the field of transportation geography, despite calls to integrate human perceptions of travel with environmental psychology and cognitive science, mainstream research still follows traditional behavioral survey methods, making it difficult to provide comprehensive and objective measurements of the complex spatio-temporal experiences of travel. Therefore, in order to provide neuroimaging evidence of human spatio-temporal perceptions of public transportation travel, nine subjects were recruited to conduct a 3-week traffic travel experiment in a real environment (Beijing city) and returned to the laboratory to undergo fMRI scans. During the scanning period subjects carefully recalled their public transportation trips. The present study uses representational similarity analysis (RSA) to reveal the first quantitative relationship between the spatial and temporal characteristics of public transportation trips and brain activity patterns. 2 Research Content In this study, to ensure high ecological validity of the results, an empirical study of public transportation trips was conducted in a real environment and fMRI scans were returned to the laboratory at the end of the trip to recall the feelings during the trip. Similar to the number of subjects in other life-record type fMRI high-level studies, this study recruited nine subjects (four males, five females, mean age 21.7 years; number of subjects) who agreed to participate in the public transportation travel experiment and to record their travel trajectories and logs. In addition, they had no history of neurological disorders and were able to participate in a recall experiment based on fMRI scans. In the public transport travel experiment: subjects were required to choose public transport for their daily trips based on a predetermined travel destination and were required to photograph key landmarks during each trip as 'anchor points' for subsequent recall experiments. The subjects were asked to record track data using a cell phone app during each trip, and to fill out a questionnaire about the trip to collect their behavioral data after completing the trip. After a week of each trip, subjects were asked to review the landmarks they had photographed and the questionnaires they had filled out to reinforce their memory of the trip. After completing all public transportation trips, subjects verbally described their subjective perceptions of all trips (Figure 1). In the fMRI scan-based recall experiment: the entire recall process was done in the MRI lab. fMRI experiments were designed using an event-related design, with each trip-related 'anchor' presented for 10 seconds, during which subjects viewed photos of landmarks taken at the starting and ending points during the trip and based on which they were able to recall the trip. They then had 3.5 seconds to key feedback on the level of detail they recalled about the trip (remember more detail/remember less detail), and all data with less detail were excluded for subsequent analysis. Then after a random 4-12 second rest process, subjects proceeded to recall the next trip (Figure 2). Figure 2 Recall experiment based on fMRI scans The core method of this study is the classical representational similarity analysis (RSA) method in cognitive neuroscience for assessing the relationship between spatiotemporal features and brain activation patterns. The method does not directly assess the relationship between spatiotemporal features and brain activation, but rather assesses the correlation between spatiotemporal feature differences and brain activation differences (Figure 3). In this study it can be specifically divided into the following three steps. First, the first step entails estimating the brain activation pattern Bap (i.e., a three-dimensional array composed of the beta values of all brain voxels at the time of recalling that trip) for each public transportation trip. In the present study, we were only interested in the activation patterns of core brain regions associated with spatiotemporal perception and situational memory, specifically the bilateral hippocampus, the parahippocampal region, and the post-splenial complex region. The activation patterns of these core regions are a subset of the brain and are represented as follows: Based on the activation patterns of these core brain regions for trip perception, we can construct a phase dissimilarity matrix (RDM) of internal brain representations. The matrix is diagonally symmetric, and each cell in the matrix represents the "distance" between the brain activation patterns of two different trip perceptions. In this study, the Euclidean distance is used to measure the "distance" between activation patterns. Next, the second step is to quantify the spatio-temporal features of the travel routes and construct a spatio-temporal feature dissimilarity matrix (STCDM) with the same dimensions and dimensions as the RDM. A total of 14 spatial features (Euclidean distance, route distance, curvature, number of turns, number of intersections, number of unique streets, deflection angle of the route from a right angle, deflection angle of the route from the destination, azimuth, degree centrality, proximity centrality, slope, number of POIs, and land use type) and 8 temporal features (travel time, waiting time, in-vehicle time, out-of-vehicle time, travel date, travel order, number of interchanges, and travel speed). These route-based spatio-temporal features were calculated based on the log and trajectory data of the subjects' public transportation trips and combined with open-source GIS data (including Beijing's road network data, POI data, digital elevation model data, and land use type data). See the original article for the specific index meaning and reference. Then, we obtained the "distance" between the spatio-temporal characteristics of two pairs of routes by simply making a difference. Such distances are compared with the brain representation distances in the same dimension. The final step is to compare two matrices of the same dimension using a nonparametric permutation test to determine which features are closely associated and significantly related to the brain representation and represent the spatio-temporal elements that we may capture during travel perception. Figure 3 Representational similarity analysis method 3 Study results For the public transportation travel experiment, we collected a total of 651 unique travel routes (Figure 4A), and the spatio-temporal characteristics of each route were quantified and calculated, and the spatio-temporal differences between travel routes were visually reflected (Figure 4BC). In addition, we examined the internal correlation between spatio-temporal features (Figure 4DE). The results show that the correlation between the individual spatial features of travel routes is high, but the correlation between the temporal features is low, which indicates the high uncertainty of public transportation travel time and cost. For the results of the RSA analysis, we first conducted statistical analysis at the individual level of the subjects and found that there were significant differences in the representation of spatio-temporal features in the brains of different subjects (see the original supplemental material). Furthermore, although subjects' brain activity patterns may be significantly correlated with multiple spatiotemporal features simultaneously, the effect sizes of these features are not high, reflecting the fact that the perception of spatiotemporal features in real environment trips is highly complex and not the only factor perceived. These results were corroborated by the subjects' behavioral investigations (verbal descriptions). When describing their perceptions of the travel route, they talked about special events that occurred during the trip, weather conditions, bus environment, and internal activities and emotions, in addition to spatio-temporal characteristics. Finally, we examined the RSA results of nine subjects at the group level and finally determined that seven spatial features (curvature of the route, number of turns, angle of deflection of the route from a right angle, angle of deflection of the route from the destination, type of land use, number of POIs and slope) and two temporal features (travel time and waiting time) correlated significantly higher than zero with the activity patterns of the core brain regions of interest (Figure 5), these findings suggest that the human brain does characterize the spatio-temporal features of the public transportation travel process. Figure 4 Results of the public transportation travel experiment. (A) All travel route trajectories. (B) Two travel route cases. (C) Spatio-temporal feature values for the two travel routes; each value is normalized to the [0,1] range. (D) Spearman correlation between spatial and temporal features. Figure 5 (A) Location of core brain regions of interest for RSA analysis in this study; (B) spatio-temporal features significantly correlated with brain activity at the group level. 4 Summary and Outlook This study has obtained the first neuroimaging evidence on the relationship between spatio-temporal perception of public transportation trips and human brain activity through an empirical research method with the help of cognitive neuroscience, showing that spatio-temporal features such as route curvature, number of turns, route angle deviation, number of POIs, land use type and slope variation, as well as travel time and waiting time are indeed closely related to human brain activity patterns. Future research in the field of cities and transportation can use neuroimaging to better explore the causal relationships between these spatiotemporal features and traffic travel behavior, facilitating a better understanding of human activity and contributing to urban planning and public transportation from an interdisciplinary perspective. References Qin, T., Dong, W., & Huang, H. (2023). Perceptions of space and time of public transport travel associated with human brain activities: A case study of bus travel in Beijing. Computers. Environment and Urban Systems, 99, 101919 ...
Read more...
Read more...
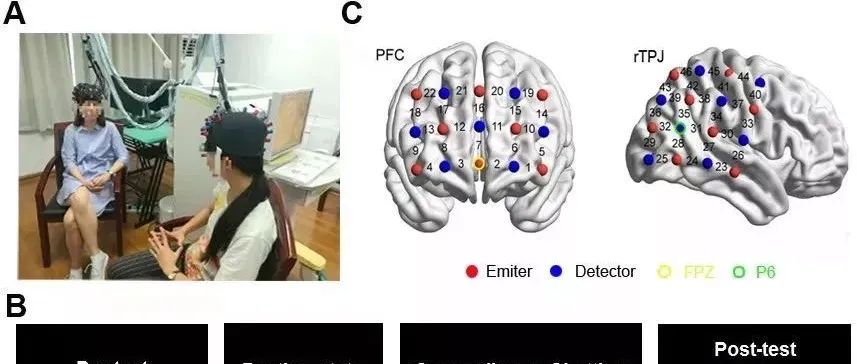
Brain science experiments prove that counseling is much more complicated than ordinary chat
Article source: School of Psychology and Cognitive Science, East China Normal University YouTube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TOfU6nnQiAU (Chinese content compiled by Simple Psychology) When it comes to counselors, the public often think that this is a particularly easy job to make a lot of money: you just need to talk to people, or even bullshit a bit, and you can easily earn hundreds to thousands of dollars per hour. You only need to talk to people, or even bullshit, you can easily earn hundreds to thousands of dollars per hour, simply to catch up with the net popularity live. But in fact, there are many experiments that have been conducted to prove scientifically thatCounseling is fundamentally different from ordinary chat in its interaction with the brain, which not only changes the emotional activity of the brain, but can even shape the brain. It's really not the simple "talk therapy" that you think of without injections or medication, sitting down and just chattering with you! Counseling and escorting on brain interaction There is a fundamental difference A study from the School of Psychology and Cognitive Science at East China Normal University used brain science experiments to demonstrate thatThere is a fundamental difference between counseling and escorting in terms of brain interaction.
Previous research has identified a great deal of behavioral synchrony between counselor and client in counseling, such as tone, head movement, body movement, facial expressions, breathing rate, skin electricity, etc. This synchrony is effective in facilitating the counseling relationship and helping to build a working alliance between client and counselor. It is important to understand that working alliance is an efficacy factor across different counseling schools, and usually refers to the degree to which the counseling partners engage in collaborative and purposeful work, which has a stable and moderate correlation with counseling outcomes. However, the brain mechanisms behind these behavioral synchronicities are poorly understood, and some researchers have proposed hypothetical models suggesting that behavioral synchrony between counselor and client may facilitate the brain synchrony between them that provides the basis for the establishment of a working alliance. That is, the better the brain match between the counselor and the visitor, the stronger the alliance. Hypotheses are hypotheses, but what is the truth? This study used functional near-red spectroscopy (fNIRS) to examine the working alliance and interpersonal brain synchronization (IBS) between counselor and visitor in a counseling situation and compared it to the interaction between the two parties in a chat situation. Thirty-four visitors were randomly assigned to either the counseling group or the chat group, and three female professional counselors provided 40 minutes of counseling or chatting with these visitors in the laboratory (Figure below). At the end of the counseling or chat, data were analyzed on the visitors' self-rated working alliance and brain synchrony between the interacting parties. The results revealed thatCompared to the chat group, subjects in the counseling group established a better working alliance after 40 minutes, matched by a stronger brain synchronization in the right temporoparietal joint area (rTPJ) (see figure below). In addition, this brain synchronization is associated with the associative component of the working alliance. The right temporoparietal joint area (rTPJ) is a brain region associated with social connectivity, cognitive synesthesia and theory of mind thatThis further supports the fact that the counseling group established a stronger emotional connection than the chat group(a component of the working alliance). In other words, counseling causes a different kind of brain activity than ordinary chatting. Moreover, the brain activity caused by counseling not only helps us build better working alliances and stronger emotional connections, but also improves our mood. Psychological counseling can change the brain's
Activity and shape A video on YouTube called Dana Foundation, using scientific data, proves to us thatCounseling can help visitors to curb negative brain activity and even change the shape of the brain.
The video describes how specific areas of the brain that control emotions are altered to varying degrees when we engage in counseling. For example, by examining the behavioral brain activity of depressed patients through fMRI brain imaging techniques, counseling can effectively reduce the activity in the part of the brain that controls sadness and depression in the amygdala - the hippocampus - and the middle prefrontal cortex. Through counseling, we can achieve a certain degree of suppression of these negative emotions, so that our intense emotions can be relieved and our mood gradually calmed down. At the same time, the video reveals the basic fact thatOur brains, like our bodies, can be "reshaped" through exercise, and if we regularly perform a brain activity, we will also grow the volume of the relevant control areas in the skull. For example, chronic anxiety and fear can increase the size of the amygdala, which controls our feelings of terror. Conversely, people with a larger amygdala are also more likely to suffer from depression (Leuchter et al., 1997). In this case, it is possible to reshape the internal shape of our brain by intervening psychologically with the symptoms. In the experiment shown in the video, people with social phobia experienced a reduction in their social phobic symptoms after receiving an online counseling session, and they showed varying degrees of reduction in amygdala volume. In other words.Counseling is also a training to strengthen our brain. If we attend more counseling, our brain will also become stronger and more resilient, and our problems can be solved better and faster. This article is from WeChat public number: Evergreen Technology EVERLOYAL ...
Read more...
Previous research has identified a great deal of behavioral synchrony between counselor and client in counseling, such as tone, head movement, body movement, facial expressions, breathing rate, skin electricity, etc. This synchrony is effective in facilitating the counseling relationship and helping to build a working alliance between client and counselor. It is important to understand that working alliance is an efficacy factor across different counseling schools, and usually refers to the degree to which the counseling partners engage in collaborative and purposeful work, which has a stable and moderate correlation with counseling outcomes. However, the brain mechanisms behind these behavioral synchronicities are poorly understood, and some researchers have proposed hypothetical models suggesting that behavioral synchrony between counselor and client may facilitate the brain synchrony between them that provides the basis for the establishment of a working alliance. That is, the better the brain match between the counselor and the visitor, the stronger the alliance. Hypotheses are hypotheses, but what is the truth? This study used functional near-red spectroscopy (fNIRS) to examine the working alliance and interpersonal brain synchronization (IBS) between counselor and visitor in a counseling situation and compared it to the interaction between the two parties in a chat situation. Thirty-four visitors were randomly assigned to either the counseling group or the chat group, and three female professional counselors provided 40 minutes of counseling or chatting with these visitors in the laboratory (Figure below). At the end of the counseling or chat, data were analyzed on the visitors' self-rated working alliance and brain synchrony between the interacting parties. The results revealed thatCompared to the chat group, subjects in the counseling group established a better working alliance after 40 minutes, matched by a stronger brain synchronization in the right temporoparietal joint area (rTPJ) (see figure below). In addition, this brain synchronization is associated with the associative component of the working alliance. The right temporoparietal joint area (rTPJ) is a brain region associated with social connectivity, cognitive synesthesia and theory of mind thatThis further supports the fact that the counseling group established a stronger emotional connection than the chat group(a component of the working alliance). In other words, counseling causes a different kind of brain activity than ordinary chatting. Moreover, the brain activity caused by counseling not only helps us build better working alliances and stronger emotional connections, but also improves our mood. Psychological counseling can change the brain's
Activity and shape A video on YouTube called Dana Foundation, using scientific data, proves to us thatCounseling can help visitors to curb negative brain activity and even change the shape of the brain.
The video describes how specific areas of the brain that control emotions are altered to varying degrees when we engage in counseling. For example, by examining the behavioral brain activity of depressed patients through fMRI brain imaging techniques, counseling can effectively reduce the activity in the part of the brain that controls sadness and depression in the amygdala - the hippocampus - and the middle prefrontal cortex. Through counseling, we can achieve a certain degree of suppression of these negative emotions, so that our intense emotions can be relieved and our mood gradually calmed down. At the same time, the video reveals the basic fact thatOur brains, like our bodies, can be "reshaped" through exercise, and if we regularly perform a brain activity, we will also grow the volume of the relevant control areas in the skull. For example, chronic anxiety and fear can increase the size of the amygdala, which controls our feelings of terror. Conversely, people with a larger amygdala are also more likely to suffer from depression (Leuchter et al., 1997). In this case, it is possible to reshape the internal shape of our brain by intervening psychologically with the symptoms. In the experiment shown in the video, people with social phobia experienced a reduction in their social phobic symptoms after receiving an online counseling session, and they showed varying degrees of reduction in amygdala volume. In other words.Counseling is also a training to strengthen our brain. If we attend more counseling, our brain will also become stronger and more resilient, and our problems can be solved better and faster. This article is from WeChat public number: Evergreen Technology EVERLOYAL ...
Read more...








































